Call Center Software CRM: A Comprehensive Guide
Call center software CRM revolutionizes customer interaction and operational efficiency. This guide delves into the essential features, implementation strategies, reporting capabilities, cost considerations, security protocols, and user experience enhancements offered by modern call center CRM systems. We explore both cloud-based and on-premise solutions, highlighting their respective strengths and weaknesses to help you make an informed decision.
From optimizing call routing and agent assignments to leveraging data analytics for performance improvement and customer satisfaction, we cover all aspects of successfully integrating and utilizing a call center CRM. We also examine the crucial role of security and compliance in protecting sensitive customer data and ensuring adherence to relevant regulations.
Call Center Software CRM Features
A robust call center software CRM system is crucial for optimizing operations, improving customer service, and driving business growth. By integrating customer interaction data with other business functions, these systems offer a holistic view of the customer journey, enabling more effective communication and personalized experiences. This leads to increased efficiency, higher customer satisfaction, and ultimately, improved bottom-line results.
Essential Features of a Robust Call Center Software CRM System
Five key features contribute significantly to the effectiveness of a call center software CRM: These features enhance agent productivity, improve customer interactions, and provide valuable insights for business decision-making.
- Call Recording and Monitoring: This feature allows supervisors to review calls for quality assurance, identify areas for improvement in agent training, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Detailed call logs provide valuable data for performance analysis.
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR): An effective IVR system routes calls efficiently, reducing wait times and improving customer satisfaction. It can also handle basic inquiries, freeing up agents to focus on more complex issues.
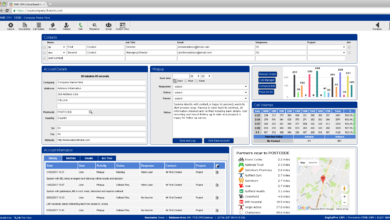
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Database: A comprehensive CRM database stores customer information, interaction history, and preferences. This allows agents to access relevant information quickly, personalize interactions, and provide more efficient service. This also facilitates targeted marketing campaigns and personalized offers.
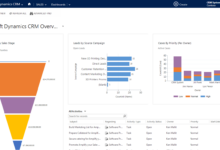
- Real-time Reporting and Analytics: Real-time dashboards provide insights into key metrics such as call volume, average handling time, and customer satisfaction scores. This allows managers to identify trends, address issues promptly, and optimize call center performance.
- Agent Performance Management: This feature tracks agent performance metrics, identifies top performers, and pinpoints areas needing improvement. It allows for targeted training and coaching, leading to increased agent productivity and improved customer service.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise Call Center CRM Solutions
The choice between cloud-based and on-premise solutions depends on specific business needs and resources. Both offer advantages and disadvantages.
| Feature | Cloud-Based | On-Premise | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Quick and easy setup, accessible from anywhere with internet connection | Requires significant upfront investment in hardware and software, installation and maintenance on-site | Cloud: Advantage – ease of deployment; Disadvantage – reliance on internet connectivity. On-Premise: Advantage – greater control over data and security; Disadvantage – high initial cost and ongoing maintenance. |
| Scalability | Easily scalable to meet changing business needs, adding or reducing resources as required | Scaling requires significant investment in additional hardware and software, potentially lengthy implementation | Cloud: Advantage – flexibility and scalability; Disadvantage – potential cost increases with rapid scaling. On-Premise: Advantage – control over scaling; Disadvantage – inflexibility and potential for over-provisioning. |
| Cost | Typically lower upfront cost, with subscription-based fees | High initial investment in hardware and software, ongoing maintenance costs | Cloud: Advantage – lower initial investment; Disadvantage – recurring subscription fees. On-Premise: Advantage – potential long-term cost savings if properly managed; Disadvantage – high initial capital expenditure. |
| Security | Relies on the cloud provider’s security infrastructure | Greater control over security measures, but requires dedicated resources for management | Cloud: Advantage – benefit from provider’s expertise and security investments; Disadvantage – reliance on third-party security. On-Premise: Advantage – greater control over security; Disadvantage – requires dedicated IT expertise and resources. |
Integration Capabilities of Call Center Software CRM
Seamless integration with other business applications significantly enhances the value of a call center software CRM. For example, integration with email marketing platforms allows for personalized email campaigns based on customer interaction history. Similarly, integration with help desk systems provides a unified view of customer issues, facilitating efficient problem resolution. This holistic approach ensures consistent customer experiences across all touchpoints. For instance, integrating with a help desk system allows agents to access and update customer tickets directly from the CRM, providing a seamless experience for both the agent and the customer. Integration with email marketing tools enables the sending of targeted emails based on customer interactions, increasing the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
Call Center Software CRM Implementation
Implementing a new call center software CRM system is a significant undertaking that requires careful planning and execution. Success hinges on a well-defined strategy encompassing thorough planning, comprehensive training, and efficient data migration. A phased approach, prioritizing key functionalities and user groups, minimizes disruption and maximizes adoption.
Implementing a new CRM system involves a series of interconnected steps. Failure to adequately address any one of these steps can lead to delays, cost overruns, and ultimately, a system that fails to meet its intended purpose. A structured approach is crucial for a smooth transition.
Planning for CRM Implementation
Successful implementation begins with meticulous planning. This phase involves defining project goals, identifying stakeholders, and assembling a dedicated project team. A comprehensive needs assessment is crucial to determine the specific requirements of the call center. This includes analyzing current workflows, identifying pain points, and establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of the implementation. A realistic timeline and budget should be established, accounting for potential unforeseen challenges. The selection of the appropriate CRM system, tailored to the specific needs of the call center, is paramount. Finally, a detailed communication plan should be developed to keep all stakeholders informed throughout the process.
Data Migration Strategies
Migrating existing data from legacy systems to the new CRM is a critical step. This process requires careful planning and execution to ensure data accuracy and integrity. Data cleansing and validation are essential to eliminate duplicate or outdated information. A phased migration approach, starting with a pilot group, allows for testing and refinement before a full-scale migration. Consider the use of data mapping tools to ensure accurate data transfer and minimize errors. Post-migration data verification is necessary to confirm the accuracy and completeness of the transferred data. The development of a rollback plan, in case of unforeseen issues, is crucial for mitigating risk.
Call Center Agent Training Program
A robust training program is vital for ensuring that call center agents effectively utilize the new CRM system. The program should include both initial training and ongoing support. Initial training should cover the core functionalities of the CRM, including navigation, data entry, and reporting. Hands-on training sessions with simulated scenarios should be incorporated. Ongoing support can include regular refresher courses, access to online resources, and ongoing mentorship from experienced users. Feedback mechanisms should be implemented to identify areas where additional training or support may be needed. The training should be tailored to different skill levels and roles within the call center.
Configuring Call Routing and Agent Assignment Rules
Proper configuration of call routing and agent assignment rules is critical for optimizing call handling and ensuring efficient resource allocation. This process requires careful consideration of various factors, including call volume, agent availability, and skill sets.
- Define Call Queues: Create separate queues for different types of calls (e.g., sales, support, technical issues) to ensure calls are directed to the appropriate agents.
- Establish Skill-Based Routing: Route calls based on agent skills and expertise. This ensures that calls are handled by agents who are best equipped to address the caller’s needs.
- Implement Agent Availability Settings: Configure agent availability settings to reflect their working hours and breaks. This prevents calls from being routed to unavailable agents.
- Configure Automatic Call Distribution (ACD): Utilize ACD to distribute calls evenly among available agents, optimizing call handling efficiency.
- Set Up Call Back Functionality: Implement call back functionality to allow agents to schedule callbacks for busy or unavailable callers.
- Monitor and Adjust Routing Rules: Regularly monitor call routing performance and adjust rules as needed to optimize efficiency and caller satisfaction.
Call Center Software CRM Reporting and Analytics
Effective reporting and analytics are crucial for optimizing call center performance. Call center software CRMs offer powerful tools to track key metrics, identify areas for improvement, and ultimately enhance both agent productivity and customer satisfaction. By leveraging the data collected, businesses can make data-driven decisions to streamline operations and deliver a superior customer experience.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) Tracked by Call Center Software CRM
Understanding key performance indicators is fundamental to measuring call center effectiveness. The following table illustrates some essential KPIs, their measurement methods, and their overall importance to a successful operation.
| KPI | Description | Measurement Method | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Handle Time (AHT) | The average duration of a customer interaction, encompassing talk time, hold time, and after-call work. | Calculated by dividing the total handle time by the number of calls. | Indicates efficiency and agent effectiveness. Lower AHT generally signifies improved efficiency. |
| First Call Resolution (FCR) | The percentage of calls resolved on the first attempt without requiring further contact. | Calculated by dividing the number of calls resolved on the first attempt by the total number of calls. | A high FCR reflects improved agent training, efficient processes, and customer satisfaction. |
| Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) | A measure of how satisfied customers are with the service they received. | Typically measured through post-call surveys or feedback forms. | Crucial for gauging customer experience and identifying areas for improvement. |
| Average Speed of Answer (ASA) | The average time it takes for a call to be answered by an agent. | Calculated by dividing the total answer time by the number of calls answered. | A low ASA indicates efficient call routing and staffing levels, leading to improved customer experience. |
| Agent Occupancy | The percentage of time an agent spends actively handling calls or performing related tasks. | Calculated by dividing the total time spent on calls and related tasks by the total available time. | Helps optimize staffing levels and ensure agents are efficiently utilized. |
Using CRM Data to Improve Agent Performance and Customer Satisfaction
Call center software CRM data provides actionable insights to improve both agent performance and customer satisfaction. Analyzing data such as AHT, FCR, and CSAT scores can pinpoint areas where agents need additional training or support. For instance, consistently low FCR might indicate a need for improved product knowledge training or more efficient knowledge base access. Similarly, high AHT might suggest process inefficiencies or the need for better call handling techniques. By identifying these trends, targeted training programs and process improvements can be implemented to enhance agent skills and ultimately improve customer satisfaction. Furthermore, real-time dashboards can provide agents with immediate feedback on their performance, allowing for self-correction and continuous improvement.
Generating Custom Reports to Analyze Call Center Efficiency
Most call center software CRMs offer robust reporting and analytics functionalities enabling the generation of custom reports tailored to specific needs. For example, a manager might generate a report analyzing call volume trends over time to anticipate peak periods and optimize staffing levels. Another report might focus on individual agent performance, highlighting strengths and weaknesses to guide coaching and training efforts. By segmenting data based on various parameters like call type, agent, time of day, or customer segment, businesses can gain a granular understanding of their call center’s efficiency and identify bottlenecks or areas for improvement. These custom reports provide a powerful tool for data-driven decision-making, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and a superior customer experience. For instance, a report showing a high volume of calls related to a specific product feature could indicate a need for improved product documentation or training materials.
Call Center Software CRM Cost and ROI
Investing in a call center software CRM system represents a significant financial commitment, but the potential return on investment (ROI) can be substantial. Understanding the various cost factors and projecting potential benefits is crucial for making an informed decision. This section will outline the key cost components and provide a hypothetical scenario illustrating the potential ROI.
Cost Factors Associated with Call Center Software CRM
Implementing and maintaining a call center CRM involves several cost factors. These can be broadly categorized into initial investment and ongoing operational expenses. Careful budgeting and planning are essential to accurately estimate the total cost of ownership (TCO).
- Licensing Fees: These are recurring annual or monthly charges based on the number of users, features, and support levels selected. Pricing models vary widely among vendors, ranging from per-user subscriptions to tiered packages offering increased functionality at higher price points.
- Implementation Costs: This includes the cost of initial setup, data migration, customization, training, and integration with existing systems. This phase can be resource-intensive, involving consultant fees, internal staff time, and potential hardware upgrades.
- Ongoing Maintenance: This encompasses regular software updates, technical support, bug fixes, and system maintenance. It’s essential to factor in these ongoing costs to ensure the system remains operational and up-to-date.
- Hardware and Infrastructure: Depending on the chosen solution (cloud-based or on-premise), costs may include server hardware, network infrastructure, and associated IT support. Cloud-based solutions generally reduce these upfront costs.
Hypothetical ROI Scenario
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario for a mid-sized call center handling 10,000 calls per month. Currently, their average call handling time is 8 minutes, and they have 10 agents. Implementing a CRM system with features like automated call routing, knowledge base access, and customer interaction history could reduce average handling time by 2 minutes per call.
This translates to a reduction of 20,000 minutes per month (10,000 calls * 2 minutes/call), or approximately 333 hours. Assuming an average agent hourly cost of $25, this represents a monthly cost savings of $8,325 (333 hours * $25/hour). If the annual cost of the CRM system is $20,000, the ROI is achieved within a short timeframe. This is a simplified example; a more detailed analysis would consider factors like increased sales conversions and improved customer satisfaction.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Comparison
The following table compares the TCO for three hypothetical call center CRM vendors over a three-year period. These figures are for illustrative purposes and should not be taken as definitive pricing.
| Vendor | Licensing Fees (Annual) | Implementation Costs | Maintenance (Annual) | Total 3-Year Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vendor A | $15,000 | $10,000 | $2,000 | $71,000 |
| Vendor B | $12,000 | $8,000 | $3,000 | $63,000 |
| Vendor C | $20,000 | $5,000 | $1,000 | $71,000 |
Call Center Software CRM Security and Compliance
Protecting customer data and ensuring compliance are paramount when implementing a call center software CRM. Failure to do so can result in significant financial penalties, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust. This section details key security considerations and compliance requirements to ensure your system is both secure and legally compliant.
Choosing and implementing a secure call center CRM involves a multi-faceted approach encompassing data encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Compliance, on the other hand, requires understanding and adhering to relevant regulations such as GDPR and CCPA, which dictate how personal data is collected, processed, and protected.
Data Encryption and Access Controls
Robust data encryption is crucial for protecting sensitive customer information both in transit and at rest. This involves using strong encryption protocols like AES-256 to safeguard data from unauthorized access. Furthermore, implementing granular access controls ensures that only authorized personnel have access to specific data based on their roles and responsibilities. For instance, a customer service representative might only have access to customer interaction history, while a manager might have broader access to performance reports and agent activity. This layered approach minimizes the risk of data breaches and ensures data integrity.
Compliance with GDPR and CCPA
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) are landmark regulations that significantly impact how businesses handle personal data. GDPR, applicable across the European Union, grants individuals greater control over their personal data, including the right to access, rectification, erasure, and data portability. CCPA, applying to businesses operating in California, provides similar rights to California residents. Call center software CRMs must be configured to meet these requirements, including providing mechanisms for data subject requests, maintaining detailed records of data processing activities, and implementing appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect personal data. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines and legal repercussions.
Data Privacy and Security Best Practices
Several best practices contribute to a secure and compliant call center CRM environment. These include regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations. Employee training on data privacy and security protocols is equally essential to cultivate a security-conscious culture within the organization. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple forms of authentication before granting access to the system. Regular software updates and patching are crucial for addressing known vulnerabilities and mitigating potential security risks. Finally, a comprehensive incident response plan should be in place to effectively manage and contain security incidents should they occur. This plan should outline procedures for identifying, containing, investigating, and remediating security breaches.
Call Center Software CRM User Experience
A positive user experience is paramount for a successful call center CRM implementation. Intuitive design, coupled with effective training and ongoing support, directly impacts agent productivity, customer satisfaction, and overall operational efficiency. A poorly designed system can lead to frustration, errors, and ultimately, lost revenue. Conversely, a well-designed system empowers agents and supervisors to work more effectively, leading to improved performance metrics.
The ideal user interface should prioritize ease of navigation and access to critical information. The design should minimize the number of clicks required to complete common tasks, reducing agent frustration and improving call handling times. A visually appealing and uncluttered interface contributes to a more positive and efficient workflow.
Ideal User Interface Design
The ideal call center software CRM interface should present a clean, uncluttered dashboard providing agents with immediate access to key customer information. This includes the customer’s name, contact details, recent interaction history, and any relevant notes or flags. A prominent search bar allows for quick lookups, and a customizable layout lets agents prioritize the information most relevant to their tasks. The interface should be responsive and adapt seamlessly to various screen sizes, supporting both desktop and mobile access. Color-coding can be used to highlight important information, such as overdue tasks or urgent requests. The use of clear icons and intuitive labels helps minimize the learning curve for new users. For example, a visual representation of a customer’s history, such as a timeline showing past interactions, can significantly improve understanding and context. This visual aid helps agents quickly grasp the customer’s history, leading to more personalized and efficient interactions.
User Training and Ongoing Support
Comprehensive user training is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of any CRM system. Training should cover all aspects of the software, from basic navigation to advanced features. This can include online modules, instructor-led sessions, or a combination of both. Ongoing support is equally important, providing agents with readily available resources to address any questions or issues that arise. This can include FAQs, online help documentation, and dedicated support staff. Regular refresher training can ensure that agents stay up-to-date with any new features or updates. A robust knowledge base, easily accessible within the CRM system itself, can empower agents to resolve many issues independently. Companies like Zendesk, for instance, excel at providing extensive documentation and support resources, resulting in improved user proficiency and satisfaction.
Features Enhancing User Experience
Several features can significantly improve the overall user experience for both agents and supervisors. Real-time data dashboards, for example, provide supervisors with an overview of agent performance and call volume, allowing for proactive management and resource allocation. Integrated communication tools, such as email, chat, and social media integration, streamline communication and provide a unified view of customer interactions. Automated workflows can reduce manual tasks, freeing up agents to focus on customer interactions. Predictive dialing and intelligent routing features improve call efficiency. For instance, features like call recording and quality monitoring tools allow for performance evaluation and continuous improvement. Finally, personalized dashboards, allowing agents to customize their workspace with frequently used tools and information, contribute to greater efficiency and user satisfaction. These features, implemented thoughtfully, create a streamlined, efficient, and positive user experience.
Final Review
Implementing a robust call center software CRM system is a strategic investment that yields significant returns in enhanced customer experience, streamlined operations, and improved agent productivity. By carefully considering the features, implementation steps, reporting capabilities, cost implications, and security measures discussed in this guide, businesses can optimize their call center operations and achieve a substantial return on investment. The key is selecting a system that aligns with your specific needs and proactively managing its implementation and ongoing maintenance.