Services CRM Software: Streamlining Service Operations
Services CRM software revolutionizes how businesses manage service delivery. Unlike sales-focused CRMs, services CRM prioritizes efficient service delivery, customer satisfaction, and operational optimization. It empowers businesses to track service requests, manage field technicians, schedule appointments, and maintain comprehensive customer interaction histories, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and stronger client relationships. This comprehensive guide delves into the functionalities, benefits, and implementation of services CRM software, equipping businesses to make informed decisions about enhancing their service operations.
This exploration covers key features, from field service management and service level agreement (SLA) tracking to the integration of AI and IoT devices. We’ll also examine different pricing models, implementation strategies, and showcase successful case studies illustrating the return on investment (ROI) of adopting services CRM software. Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, understanding the nuances of services CRM is crucial for maximizing operational efficiency and customer loyalty in today’s competitive landscape.
Defining “Services CRM Software”
Services CRM software is a specialized customer relationship management system designed to streamline and optimize the delivery of services to clients. Unlike sales CRM, which focuses on acquiring new customers, services CRM prioritizes managing existing customer relationships and ensuring efficient service delivery. It aims to improve customer satisfaction, reduce operational costs, and enhance the overall service experience.
Services CRM software provides a centralized platform for managing all aspects of service delivery, from initial contact to post-service follow-up. This includes tracking service requests, managing technician schedules, monitoring service level agreements (SLAs), and gathering customer feedback. The software’s core functionality is built around improving efficiency and effectiveness in providing services.
Core Functionalities of Services CRM Software
The core functionalities of services CRM software revolve around enhancing service delivery and customer satisfaction. Key features typically include: ticketing and request management, scheduling and dispatch, knowledge base management, self-service portals, and reporting and analytics. Ticketing systems allow for efficient tracking of service requests, ensuring no request falls through the cracks. Scheduling and dispatch features optimize technician routing and workload, minimizing travel time and improving response times. A robust knowledge base empowers both technicians and customers with quick access to solutions, reducing resolution times and improving self-service capabilities. Finally, comprehensive reporting and analytics provide valuable insights into service performance, helping businesses identify areas for improvement.
Key Differences Between Services CRM and Sales CRM
While both services CRM and sales CRM are types of CRM, their focuses differ significantly. Sales CRM primarily concentrates on lead generation, sales pipeline management, and closing deals. It emphasizes acquiring new customers. Services CRM, conversely, focuses on managing existing customer relationships and ensuring efficient service delivery. It prioritizes customer retention and satisfaction. Sales CRM might track opportunities and sales stages, while services CRM tracks service requests, resolution times, and customer satisfaction scores. The metrics used to measure success are also different: sales CRM tracks revenue and conversion rates, while services CRM focuses on customer satisfaction, first-call resolution rates, and average resolution times.
Businesses That Benefit Most From Services CRM Software
Numerous industries benefit from implementing services CRM software. Companies providing field services, such as HVAC repair, plumbing, or electrical work, greatly benefit from the scheduling and dispatch capabilities. IT support companies utilize it to manage help desk tickets and track resolution times. Telecommunications companies use it for managing customer inquiries and technical support issues. Even companies offering less tangible services, such as consulting or training, can use services CRM to track project progress, manage client communication, and measure client satisfaction. Essentially, any business that provides ongoing services to clients can leverage services CRM to improve efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Comparison of Popular Services CRM Software Options
Here’s a comparison of three popular services CRM software options:
| Software Name | Key Features | Pricing Model | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Freshdesk | Ticketing system, self-service portal, knowledge base, reporting and analytics, integrations with other tools | Subscription-based, various plans available | Small to medium-sized businesses, particularly those in IT support and customer service |
| Zendesk | Ticketing system, omnichannel support, agent collaboration tools, analytics dashboards, app marketplace | Subscription-based, various plans available | Businesses of all sizes, with a strong focus on customer service and support |
| Salesforce Service Cloud | Case management, knowledge base, field service management, community forums, AI-powered features | Subscription-based, various plans available | Large enterprises and businesses with complex service needs |
Features and Benefits of Services CRM Software
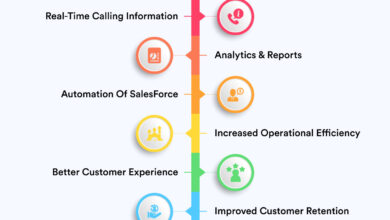
Services CRM software offers a powerful suite of tools designed to optimize service delivery, enhance customer relationships, and boost overall business efficiency. By integrating various aspects of service management into a centralized platform, businesses can streamline operations, improve communication, and ultimately deliver a superior customer experience. This results in increased customer satisfaction, reduced operational costs, and improved profitability.
Field Service Management in Services CRM
Field service management (FSM) is a crucial component of effective services CRM. It encompasses the planning, scheduling, dispatching, and monitoring of technicians or service professionals who perform work on-site for clients. Integrating FSM capabilities directly within the CRM system provides a unified view of all service activities, improving communication and collaboration between office staff and field personnel. For instance, a technician can update a job status in real-time, automatically notifying the customer and updating the central database. This real-time visibility allows for efficient resource allocation, quicker response times, and improved overall service delivery. The system can also optimize routing and scheduling based on technician location, skill sets, and customer priorities, minimizing travel time and maximizing productivity.
Impact of Service Level Agreements (SLAs) on Software Selection
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are critical contracts outlining the expected performance levels of a service provider. When selecting services CRM software, it’s vital to ensure the software can effectively manage and track SLAs. The chosen software should offer features that allow businesses to define, monitor, and report on key SLA metrics, such as response times, resolution times, and first-contact resolution rates. For example, the software might generate automated alerts when an SLA is at risk of being breached, allowing for proactive intervention. The ability to track and report on SLA performance is crucial for demonstrating compliance, identifying areas for improvement, and maintaining positive customer relationships. Software lacking robust SLA management capabilities may lead to missed deadlines, dissatisfied customers, and potential contractual penalties.
Key Features Improving Customer Satisfaction
Several key features within services CRM software directly contribute to enhanced customer satisfaction. These features enable efficient communication, personalized service, and proactive problem-solving. For example, self-service portals allow customers to access information, track service requests, and communicate directly with support staff, fostering a sense of control and empowerment. Automated notifications and reminders keep customers informed about the progress of their service requests, minimizing uncertainty and anxiety. Comprehensive case management tools enable technicians and support staff to maintain detailed records of customer interactions and service history, facilitating personalized and efficient service delivery. Furthermore, features such as integrated knowledge bases provide quick access to solutions, reducing resolution times and improving overall customer experience.
Streamlining Scheduling and Dispatch
Services CRM software streamlines scheduling and dispatch through various functionalities. Automated scheduling tools optimize technician routes and assignments based on factors such as location, skills, availability, and service request priorities. Real-time tracking capabilities provide visibility into technician location and progress, allowing dispatchers to manage workloads effectively and respond to unexpected issues promptly. For instance, if a technician encounters an unforeseen delay, the system can automatically reschedule appointments and notify affected customers, minimizing disruptions. Integration with mapping and navigation tools further enhances efficiency by providing optimized routes and reducing travel time. This integrated approach minimizes scheduling conflicts, improves response times, and enhances the overall efficiency of field service operations.
Implementation and Integration of Services CRM Software
Implementing a services CRM system requires careful planning and execution to ensure a smooth transition and maximize its benefits. This involves a phased approach, considering your business’s specific needs and existing infrastructure. Successful integration with existing systems is crucial for avoiding data silos and maximizing efficiency.
Step-by-Step Implementation Plan for a Small Business
A phased approach is recommended for small businesses to minimize disruption and allow for adjustments along the way. This plan outlines key steps and considerations.
- Needs Assessment and Software Selection: Begin by identifying your specific service-related needs and challenges. This involves analyzing your current processes, identifying pain points, and defining your goals for the CRM. Based on this analysis, research and select a CRM system that aligns with your budget, technical capabilities, and future scalability needs. Consider factors like ease of use, integration capabilities, and available support.
- Data Migration and Cleansing: Before launching, carefully plan the migration of existing customer data. This often involves data cleansing to ensure accuracy and consistency. This step is critical to avoid data errors and inconsistencies within the new system.
- System Configuration and Customization: Configure the chosen CRM system to match your business processes. This may involve customizing workflows, creating custom fields, and integrating with other systems. Ensure the system accurately reflects your service delivery processes.
- User Training and Adoption: Invest in comprehensive user training to ensure staff understands and effectively utilizes the new system. Provide ongoing support and address any challenges encountered during the initial adoption phase.
- Go-Live and Monitoring: Launch the CRM system in a controlled manner, perhaps starting with a pilot group before a full rollout. Monitor system performance, user adoption rates, and identify areas for improvement. Regularly review and adjust your implementation strategy based on feedback and performance data.
Integrating Services CRM with Existing Business Systems
Seamless integration with existing systems, such as accounting software, helpdesk ticketing systems, and marketing automation tools, is key to maximizing the value of a services CRM. This avoids data duplication and ensures a unified view of the customer.
Integration methods vary depending on the CRM and existing systems. Common approaches include APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), which allow for direct data exchange, and pre-built connectors or integrations offered by the CRM vendor or third-party providers. For example, a popular accounting software like Xero might offer a pre-built integration with many CRM platforms, simplifying the process significantly. A poorly integrated system can lead to significant inefficiencies and data discrepancies.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise Services CRM Solutions
The choice between cloud-based and on-premise solutions depends on various factors, including budget, IT infrastructure, and security requirements.
| Feature | Cloud-Based | On-Premise |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Typically lower upfront costs, subscription-based | Higher upfront investment in hardware and software |
| Scalability | Easily scalable to meet changing needs | Requires significant investment to scale |
| Maintenance | Vendor handles maintenance and updates | Requires internal IT resources for maintenance and updates |
| Accessibility | Accessible from anywhere with internet access | Limited to internal network access |
| Security | Vendor responsible for security, but data breaches are possible | Greater control over security, but requires robust internal security measures |
Potential Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Implementing a services CRM can present several challenges. Proactive planning and mitigation strategies are crucial for a successful implementation.
- Data Migration Issues: Inconsistent or incomplete data can hinder the effectiveness of the CRM. Solution: Thorough data cleansing and validation before migration.
- User Adoption Resistance: Staff resistance to change can slow down adoption. Solution: Comprehensive training, clear communication, and addressing concerns proactively.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating with existing systems can be technically challenging. Solution: Choose a CRM with robust integration capabilities and consider professional integration services.
- Cost Overruns: Unexpected costs can arise during implementation. Solution: Develop a detailed budget and carefully track expenses.
- Lack of Training and Support: Inadequate training can lead to low user adoption. Solution: Invest in comprehensive training programs and provide ongoing support.
Choosing the Right Services CRM Software
Selecting the appropriate Services CRM software is crucial for optimizing business operations and enhancing customer relationships. A poorly chosen system can lead to inefficiencies, data silos, and ultimately, lost revenue. Therefore, a thorough assessment of your business needs is paramount before committing to any specific software.
Assessing Business Needs
Before diving into software evaluations, thoroughly analyze your business’s unique requirements. Consider the size and structure of your service team, the complexity of your service offerings, the volume of customer interactions, and your current technological infrastructure. Identify key pain points in your existing service processes – are you struggling with ticket management, communication delays, or reporting inefficiencies? These pain points will guide your selection of features and functionalities. For example, a small business with a simple service offering will have vastly different needs than a large enterprise with multiple service levels and complex workflows.
Essential Features Checklist
A comprehensive evaluation should include a checklist of essential features. Prioritize features directly addressing your identified pain points. This checklist should include:
- Ticket Management: Robust ticket creation, assignment, prioritization, and tracking capabilities are essential for efficient service delivery.
- Knowledge Base Integration: Seamless integration with a knowledge base allows agents to quickly access information and resolve issues efficiently.
- Self-Service Portal: A customer self-service portal empowers customers to find answers and resolve issues independently, reducing the workload on your support team.
- Reporting and Analytics: Comprehensive reporting tools provide insights into key performance indicators (KPIs) such as resolution times, customer satisfaction, and agent productivity.
- Automation Features: Automation features such as automated email responses, workflow rules, and task assignments can significantly improve efficiency.
- Integration Capabilities: The ability to integrate with other business systems, such as billing and accounting software, is critical for a seamless workflow.
- Mobile Accessibility: Access to the CRM system from mobile devices allows agents to respond to customer requests quickly, regardless of location.
Evaluating Vendor Reliability and Support
Vendor reliability and support are paramount. Investigate the vendor’s reputation, financial stability, and customer reviews. Look for vendors with a proven track record of successful implementations and strong customer support. Request demos and trials to assess the user-friendliness of the software and the responsiveness of the support team. Check for service level agreements (SLAs) guaranteeing uptime and response times. Consider factors like the vendor’s location and their ability to provide support in your time zone.
Pricing Models and Implications
Choosing the right pricing model is critical for budget management. Different models cater to varying business needs and scales.
| Pricing Model | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subscription (per user/month) | Recurring monthly fee based on the number of users. | Predictable costs, scalable, often includes updates and support. | Can become expensive with a large team, features may be limited by plan. |
| One-time purchase | A single upfront payment for the software license. | Lower initial cost, potentially full feature access. | No ongoing support or updates typically included, higher upfront investment. |
| Tiered pricing | Different pricing plans offering varying features and functionalities. | Flexibility to choose a plan that fits your budget and needs. | Can be confusing to compare plans, may require upgrades as needs evolve. |
| Usage-based pricing | Charges based on the actual usage of the software. | Pay only for what you use, cost-effective for businesses with fluctuating usage. | Difficult to predict costs accurately, potential for unexpected charges. |
Advanced Features and Emerging Trends
Services CRM software is rapidly evolving, incorporating cutting-edge technologies to enhance efficiency and customer satisfaction. The integration of artificial intelligence, mobile accessibility, and the Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming how businesses manage service operations and interact with their clients. This section explores these advanced features and the emerging trends shaping the future of service CRM.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Enhancing Service Operations
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing service operations by automating tasks, improving predictive capabilities, and personalizing customer interactions. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of customer data to identify patterns and predict potential issues, enabling proactive service interventions. For instance, a service CRM system using machine learning might predict equipment failures based on historical usage data, allowing for preventative maintenance and minimizing downtime. AI-powered chatbots can handle routine customer inquiries, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues. This leads to faster response times, reduced operational costs, and improved customer satisfaction. Furthermore, AI can personalize service recommendations based on individual customer preferences and past interactions, creating a more tailored and valuable experience.
Mobile Apps for Field Technicians and Customers
Mobile apps are essential components of modern service CRM systems, providing field technicians and customers with convenient access to information and tools. For field technicians, mobile apps offer real-time access to customer information, service history, and work orders, streamlining their workflow and improving efficiency. They can update job status, access schematics, and capture photos or videos of completed work directly from the field. For customers, mobile apps provide self-service capabilities such as scheduling appointments, tracking service requests, and accessing support documentation. This empowers customers to manage their service needs independently, reducing the burden on customer service teams. Companies like Fieldwire and ServiceTitan exemplify this trend, offering robust mobile apps integrated with their CRM platforms to enhance field service operations.
Integration of IoT Devices with Services CRM Software
The integration of IoT devices with services CRM software allows for real-time monitoring of equipment and assets, providing valuable insights into their performance and potential issues. Sensors embedded in equipment can transmit data on temperature, pressure, vibration, and other parameters to the CRM system. This data can be analyzed to identify potential problems before they escalate into major failures, enabling proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime. For example, a smart refrigerator equipped with IoT sensors could transmit data on its internal temperature and compressor performance to a service CRM system. If the system detects an anomaly, it can automatically generate a service request, alerting technicians to the potential issue before it affects the customer. This proactive approach minimizes disruptions and enhances customer satisfaction.
Examples of Proactive Customer Service Facilitated by Services CRM Software
Proactive customer service focuses on anticipating and addressing customer needs before they become problems. Services CRM software plays a crucial role in enabling this approach. By analyzing customer data and identifying patterns, the system can predict potential issues and initiate appropriate actions. For example, if a customer consistently experiences problems with a specific product feature, the system can proactively reach out to offer assistance or suggest solutions. Similarly, if a customer’s service contract is nearing expiration, the system can automatically send a renewal reminder. Predictive analytics within the CRM can also identify customers at risk of churning and trigger targeted interventions to retain their business. These proactive measures enhance customer loyalty and strengthen the customer relationship.
Case Studies and Examples
Real-world applications demonstrate the transformative power of Services CRM software. Analyzing successful implementations reveals tangible benefits and provides valuable insights for potential adopters. This section presents a detailed case study illustrating how a company leveraged Services CRM to enhance efficiency and customer satisfaction.
The following case study focuses on “Acme Tech Support,” a mid-sized company providing technical support for a range of software products. Prior to implementing a Services CRM system, Acme struggled with inefficient ticket management, inconsistent service levels, and difficulty tracking key performance indicators (KPIs).
Acme Tech Support: A Services CRM Success Story
Acme Tech Support implemented a cloud-based Services CRM solution to address its operational challenges. The software integrated seamlessly with their existing ticketing system, enabling technicians to access customer information, service history, and relevant knowledge base articles instantly. This improved response times and reduced resolution times significantly. The system also automated several key processes, such as assigning tickets, sending automated updates, and generating reports.
Before implementing the Services CRM, Acme’s average ticket resolution time was 48 hours, and customer satisfaction scores were consistently below average. Following implementation, the average ticket resolution time dropped to 24 hours, a 50% improvement. Customer satisfaction scores increased by 20%, reflecting a significant improvement in service quality.
Quantifiable Results and Return on Investment (ROI)
The implementation of the Services CRM resulted in several quantifiable improvements for Acme Tech Support. These improvements translated directly into a strong return on investment (ROI).
The following table summarizes the key performance indicators (KPIs) before and after the implementation of the Services CRM software:
| KPI | Before Implementation | After Implementation | % Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Ticket Resolution Time | 48 hours | 24 hours | -50% |
| Customer Satisfaction Score | 70% | 90% | +20% |
| Technician Productivity (Tickets Resolved per Day) | 10 | 15 | +50% |
| Support Costs per Ticket | $50 | $35 | -30% |
The reduction in support costs, coupled with the increase in technician productivity and customer satisfaction, resulted in a significant ROI. Acme estimated a 30% reduction in overall support costs within the first year, exceeding their initial investment in the software and implementation.
Key Takeaways from the Acme Tech Support Case Study
The Acme Tech Support case study highlights several crucial aspects of successful Services CRM implementation:
- Improved Efficiency: Automated processes and streamlined workflows led to significant gains in technician productivity and reduced resolution times.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Faster response times, personalized service, and proactive communication resulted in higher customer satisfaction scores.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Real-time data and reporting capabilities enabled Acme to identify areas for improvement and optimize their support processes.
- Strong ROI: The reduction in support costs and increase in efficiency generated a substantial return on investment.
- Seamless Integration: Integrating the Services CRM with existing systems minimized disruption and ensured a smooth transition.
Wrap-Up
Implementing the right services CRM software can significantly transform a business’s service operations. By carefully considering factors like specific business needs, essential features, vendor reliability, and integration capabilities, businesses can optimize service delivery, boost customer satisfaction, and achieve a strong return on investment. The journey from identifying the need for a services CRM to its successful implementation and ongoing optimization represents a strategic move towards enhanced efficiency and customer-centric operations. This guide serves as a roadmap to navigate this transformation successfully.