CRM Software for Call Center: Enhanced Efficiency
CRM software for call center operations represents a significant advancement in customer service and operational efficiency. Integrating CRM systems allows businesses to streamline call routing, manage customer interactions effectively across multiple channels, and gain valuable insights from detailed performance analytics. This sophisticated approach not only improves agent productivity but also enhances the overall customer experience, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
The seamless integration of CRM with existing call center technologies such as phone systems and IVR further optimizes workflows. By centralizing customer data and interaction history, CRM empowers agents to provide more personalized and informed support. This centralized approach also facilitates better call distribution, minimizing wait times and improving response times. The result is a more efficient and customer-centric call center operation.
Call Center Software Features
Effective call center management hinges on robust CRM software. A well-integrated CRM system streamlines operations, improves agent performance, and ultimately enhances customer satisfaction. This section will explore the key features of CRM software designed for call centers, comparing cloud and on-premise solutions, examining integration capabilities, and demonstrating how CRM software boosts agent productivity.
Essential CRM Features for Call Centers
A comprehensive CRM for call centers should offer a suite of features designed to optimize agent performance and improve customer interactions. These include features such as contact management (including detailed customer history, interaction logs, and notes), call routing and queuing (to manage call volume and ensure efficient distribution), interactive voice response (IVR) integration (to automate initial customer interactions), real-time monitoring and reporting (to track key performance indicators like average handling time and customer satisfaction), and reporting and analytics (providing valuable insights into call center performance). Furthermore, features like automated call logging and scripting, along with predictive dialing, significantly improve agent efficiency. Finally, integration with other communication channels, such as email and chat, creates a unified customer view.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise CRM Solutions
The choice between cloud-based and on-premise CRM solutions depends heavily on a call center’s specific needs and resources. Cloud-based CRM offers scalability, accessibility, and reduced upfront costs. Updates and maintenance are handled by the provider, minimizing IT overhead. On the other hand, on-premise solutions provide greater control over data security and customization options. However, they require significant upfront investment in hardware and software, ongoing maintenance, and dedicated IT staff. For example, a rapidly growing startup might benefit from the scalability of a cloud-based solution, while a large financial institution with stringent security requirements might opt for an on-premise system.
CRM Integration with Call Center Technologies
Seamless integration with existing call center technologies is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of a CRM system. This includes integration with phone systems (allowing agents to access customer information directly within their phone interface), IVR systems (allowing for automated routing and data capture), and other communication channels (like email and chat). For example, integrating the CRM with a phone system enables agents to instantly view a customer’s complete history and previous interactions before answering a call, leading to more personalized and efficient service. This integration eliminates the need for agents to manually search for information, saving valuable time and improving customer experience.
Enhancing Agent Productivity with CRM Software
CRM software significantly enhances agent productivity through automation and streamlined workflows. Features such as automated call logging, call scripting, and predictive dialing reduce manual tasks, freeing up agents to focus on customer interactions. Real-time dashboards provide agents with immediate insights into key performance indicators, enabling them to track their progress and identify areas for improvement. Furthermore, centralized customer data eliminates the need for agents to search across multiple systems, reducing call handling times and improving overall efficiency. For example, a CRM with built-in knowledge base access empowers agents to quickly resolve customer queries, improving first-call resolution rates.
Comparison of Leading CRM Software Options
| CRM Software | Key Features | Pricing Tiers | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salesforce Service Cloud | Comprehensive features, robust integrations, excellent scalability | Variable, depending on features and users | Large enterprises with complex needs |
| Zendesk Support | User-friendly interface, strong omnichannel capabilities, affordable pricing | Multiple tiers, from basic to enterprise | Small to medium-sized businesses |
| Freshdesk | Intuitive design, excellent automation features, competitive pricing | Various plans catering to different needs | Businesses seeking a balance between features and cost |
| HubSpot Service Hub | Strong integration with other HubSpot tools, free plan available | Free, starter, professional, enterprise | Businesses already using HubSpot or seeking an all-in-one solution |
| Zoho CRM | Cost-effective, comprehensive features, good scalability | Various plans with different feature sets | Businesses looking for a balance of features and affordability |
Call Routing and Management
Effective call routing and management are critical for optimizing call center efficiency and enhancing customer experience. A robust CRM system provides the tools to strategically direct calls, minimize wait times, and ensure that agents are handling calls within their expertise. This leads to increased agent productivity and improved customer satisfaction.
Call Routing Strategies
CRM software supports a variety of call routing strategies, each designed to meet specific business needs and optimize resource allocation. These strategies determine how incoming calls are directed to available agents. Common strategies include:
- Round Robin: Calls are distributed sequentially to available agents. This ensures fair distribution of workload among the team.
- Least Calls: The call is routed to the agent with the fewest active calls. This minimizes agent workload and potential for call abandonment.
- Skill-Based Routing: Calls are directed to agents possessing the necessary skills or expertise to handle the specific issue or inquiry. This improves first-call resolution rates.
- Priority Routing: Calls are prioritized based on pre-defined criteria, such as customer VIP status or urgency of the issue. This ensures that high-priority calls are addressed promptly.
- Time-Based Routing: Calls are routed to agents based on their availability during specific time periods. This allows for efficient management of shifts and staffing levels.
Improving Call Distribution and Reducing Wait Times
CRM systems significantly enhance call distribution by providing real-time visibility into agent availability, call queue lengths, and call handling times. Features like automatic call distribution (ACD) and predictive dialing optimize call flow, minimizing wait times and improving customer satisfaction. For example, a CRM system could automatically route a call about a billing issue to an agent specializing in billing inquiries, rather than a general support agent, resulting in a faster resolution. Furthermore, real-time queue monitoring allows supervisors to identify bottlenecks and adjust agent assignments dynamically to manage call volume fluctuations.
Best Practices for Configuring Call Routing Rules
Effective configuration of call routing rules requires careful consideration of various factors, including call volume patterns, agent skill sets, and service level agreements (SLAs). Best practices include:
- Regularly review and adjust routing rules: Call patterns change over time, necessitating periodic adjustments to routing rules to maintain optimal performance.
- Utilize skill-based routing effectively: Ensure that agent skills are accurately reflected in the system to ensure calls are directed to the most appropriate agent.
- Monitor key metrics: Track call handling times, average wait times, and abandonment rates to identify areas for improvement in routing rules.
- Implement a robust reporting system: Regularly analyze call routing data to identify trends and make data-driven decisions to optimize routing rules.
- Consider implementing IVR (Interactive Voice Response) systems: IVR systems can pre-qualify calls and route them to the appropriate agents based on caller input, further improving efficiency.
Managing Call Queues and Agent Availability
CRM software plays a crucial role in managing call queues and agent availability by providing a centralized view of all active calls, agent status, and queue lengths. This allows supervisors to monitor performance in real-time, identify potential issues, and proactively manage resources. For instance, if a queue is consistently exceeding the target wait time, the supervisor can add agents to the queue or adjust routing rules to alleviate the backlog. Furthermore, the system can track agent breaks, lunches, and other absences, ensuring that calls are only routed to available agents.
Setting Up Automated Call Distribution (ACD)
Setting up ACD within a CRM system involves a series of steps to configure the routing rules and integrate the system with the phone system.
- Define Agent Skills and Availability: Input agent profiles including their skills, availability, and assigned queues.
- Configure Call Routing Rules: Establish the logic for distributing calls based on factors like skill, priority, and availability. This might involve using a combination of routing strategies mentioned previously.
- Integrate with Phone System: Connect the CRM system to the phone system via API or other integration methods to enable seamless call routing.
- Test and Monitor: Thoroughly test the ACD setup to ensure it functions correctly and monitor key metrics to identify areas for improvement. Regularly review and adjust the settings based on performance data.
- Implement Call Back Features: Configure call back options for callers who experience long wait times, reducing abandonment rates.
Customer Interaction and Data Management
Effective CRM software is the backbone of a successful call center, streamlining customer interactions and optimizing data management across various communication channels. It allows agents to access crucial information instantly, personalize interactions, and improve overall customer service efficiency. This section details how CRM software facilitates seamless customer interaction and data management.
CRM software revolutionizes how call centers manage customer interactions by unifying communication across multiple platforms. Instead of siloed systems for phone calls, emails, and chats, a centralized CRM provides a single view of each customer interaction, regardless of the channel used. This unified approach improves agent efficiency by eliminating the need to switch between applications and provides a more consistent and personalized customer experience.
Customer Data Access During Calls
CRM software integrates directly with the call center’s phone system, allowing agents to access a customer’s complete profile, including past interactions, purchase history, and preferences, the moment a call connects. This immediate access to relevant data empowers agents to provide personalized service, address customer needs efficiently, and resolve issues quickly. For example, if a customer calls about a previous order, the agent can instantly see the order details, shipping status, and any previous communications related to that order, preventing unnecessary delays and frustration.
Tracking Customer Interactions and Building a History
CRM systems meticulously track every interaction a customer has with the call center. This includes detailed timestamps, call duration, agent notes, and even recordings of the calls themselves (with appropriate consent). This comprehensive interaction history is automatically linked to the customer’s profile, creating a complete timeline of their relationship with the company. This data is invaluable for identifying trends, improving service quality, and personalizing future interactions. The system might, for example, automatically flag customers who have contacted the call center multiple times about the same issue, prompting the agent to take a more proactive approach to resolution.
Benefits of CRM Integration with Other Tools
Integrating CRM software with other customer relationship management tools, such as marketing automation platforms or social media monitoring tools, enhances its capabilities significantly. For example, integrating with a marketing automation platform allows for personalized email campaigns based on customer interactions, while integrating with social media monitoring tools allows agents to see any public comments or complaints a customer has made, providing context for the call. This holistic view of the customer empowers agents to provide more informed and effective support.
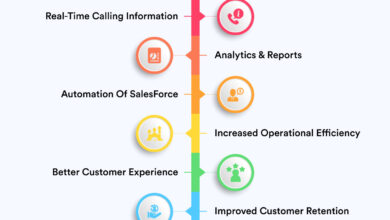
Ways CRM Software Improves Customer Service in Call Centers
The integration of CRM software offers several key advantages for call centers aiming to enhance customer service. These improvements contribute to increased efficiency, higher customer satisfaction, and ultimately, stronger customer relationships.
- Reduced call handling times: Quick access to customer data allows agents to resolve issues faster.
- Improved first call resolution: Agents have all the necessary information at their fingertips, reducing the need for multiple calls.
- Personalized customer experiences: Agents can tailor their interactions based on individual customer preferences and history.
- Increased customer satisfaction: Faster resolution times and personalized service lead to happier customers.
- Enhanced agent productivity: Streamlined workflows and access to information improve agent efficiency.
- Better data-driven decision making: Comprehensive interaction data provides valuable insights for service improvements.
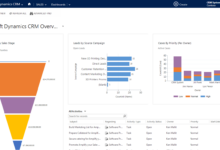
Reporting and Analytics
Effective CRM software provides robust reporting and analytics capabilities, offering invaluable insights into call center performance and paving the way for data-driven improvements. This data-driven approach allows for informed decision-making, optimized resource allocation, and ultimately, improved customer service and increased profitability.
CRM software generates reports on key call center performance metrics by tracking various data points throughout the customer interaction lifecycle. This includes call duration, hold times, agent performance, customer satisfaction scores (CSAT), first call resolution (FCR) rates, and average handling time (AHT). The software aggregates this data and presents it in customizable reports, dashboards, and visualizations, enabling managers to easily monitor performance trends and identify areas needing attention.
Actionable Insights from CRM Analytics
CRM analytics provide actionable insights that directly impact operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. For instance, analyzing AHT trends can reveal bottlenecks in the call handling process. High AHT might indicate a need for improved agent training, updated knowledge bases, or more efficient call routing strategies. Similarly, low FCR rates suggest opportunities to refine processes, improve agent product knowledge, or develop more effective troubleshooting techniques. Analyzing customer feedback through CSAT scores helps identify areas where customer experience can be enhanced. For example, consistently low CSAT scores related to hold times indicate a need for additional staffing or improved call queuing systems.
Using CRM Data to Identify Areas for Improvement
CRM data offers a powerful tool for identifying specific areas for improvement within call center operations. By analyzing call recordings and agent performance metrics, managers can pinpoint specific training needs or coaching opportunities. For example, consistent issues with a particular product or service could highlight the need for updated training materials or process improvements. Identifying patterns in customer complaints can reveal recurring problems that require attention, such as faulty products or confusing processes. Analyzing call volume trends can help predict peak periods and optimize staffing levels to ensure adequate coverage during high-demand times. This proactive approach minimizes wait times and improves customer satisfaction.
Demonstrating ROI and Justifying Investments with CRM Reporting
Comprehensive CRM reporting plays a crucial role in demonstrating the return on investment (ROI) of call center technology. By tracking key metrics before and after implementing a CRM system, organizations can quantify the improvements in efficiency, customer satisfaction, and cost savings. For example, a reduction in AHT directly translates to cost savings in terms of reduced labor costs. Improved FCR rates lead to increased customer satisfaction and potentially reduced call volume. These quantifiable improvements can be used to justify further investments in call center technology and demonstrate the value of CRM software to stakeholders.
Sample Call Center Performance Report
| Metric | Target | Actual | Variance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Handling Time (AHT) | 5 minutes | 4.8 minutes | -0.2 minutes |
| First Call Resolution (FCR) | 80% | 85% | +5% |
| Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) | 90% | 92% | +2% |
| Average Speed of Answer (ASA) | 20 seconds | 18 seconds | -2 seconds |
Integration with Other Systems
Seamless integration with other business systems is crucial for maximizing the value of your call center CRM. By connecting your CRM to other applications, you create a unified view of your customer, streamlining operations and improving decision-making. This interconnectedness allows for automated workflows, reduced data entry, and a more holistic understanding of customer interactions.
Integrating your CRM with other systems offers significant advantages in terms of efficiency and data accuracy. The benefits extend beyond simple data synchronization; it enables a more comprehensive approach to customer relationship management, leading to enhanced customer satisfaction and improved business outcomes.
Benefits of System Integration
Connecting your CRM to systems like ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and marketing automation platforms provides several key benefits. ERP integration allows for real-time access to inventory levels, order history, and shipping information, enriching the customer interaction with accurate and up-to-date details. Marketing automation integration allows for personalized campaigns based on CRM data, improving marketing ROI and targeting effectiveness. This synergy between systems results in a more efficient and informed approach to customer management. For example, a sales representative can access a customer’s complete order history and past interactions directly within the CRM, leading to more personalized and effective sales conversations.
Seamless Data Flow and Efficiency Improvements
The seamless flow of data between integrated systems significantly improves overall efficiency. Imagine a scenario where a customer places an order through your website. This order information automatically updates in your ERP, CRM, and inventory management systems. Your call center agents then have immediate access to order status and can proactively address any customer inquiries regarding their order. This eliminates the need for manual data entry and reduces the risk of errors, saving time and improving accuracy. Furthermore, automated workflows triggered by CRM data updates in other systems, such as sending automated order confirmation emails or scheduling follow-up calls, enhance efficiency and customer experience.
Technical Aspects of CRM Integration
Integrating CRM software with various platforms often involves using APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). APIs act as bridges, allowing different systems to communicate and exchange data. Common integration methods include real-time data synchronization, batch processing, and message queues. The specific technical approach depends on the capabilities of the individual systems and the complexity of the data exchange. For example, integrating with a cloud-based ERP system might involve using RESTful APIs, while integrating with a legacy on-premise system may require more complex solutions, such as ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes. Security considerations are paramount, requiring careful attention to data encryption and access control throughout the integration process.
Challenges and Solutions for Legacy System Integration
Integrating CRM software with legacy systems can present unique challenges. Legacy systems often lack modern APIs and may rely on outdated data formats. This can make data exchange complex and require custom development. Furthermore, legacy systems might not be scalable or flexible enough to handle the volume of data exchanged with a modern CRM. Solutions include using middleware to bridge the gap between the legacy system and the CRM, employing ETL processes to transform data into a compatible format, or gradually replacing the legacy system with a more modern, integrated solution. Careful planning and a phased approach are crucial for successful integration with legacy systems, minimizing disruption to ongoing operations.
Data Flow Between CRM and Other Systems
A flowchart illustrating the data flow would show a central CRM system connected to various other applications, such as an ERP system, a marketing automation platform, and a customer support ticketing system. Arrows would depict the flow of information, such as customer data from the CRM being used to personalize marketing emails in the marketing automation platform, or order details from the ERP being updated in the CRM to provide call center agents with real-time order status. The flowchart would clearly show how data flows seamlessly between systems, providing a visual representation of the interconnectedness and efficiency gains achieved through integration.
Security and Compliance
In today’s data-driven world, the security and compliance of customer information are paramount for any call center utilizing CRM software. Breaches can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Robust security measures are not just a best practice; they are a necessity.
Data security in call center CRM software is crucial because it protects sensitive customer information, including Personally Identifiable Information (PII) such as names, addresses, financial details, and health records. A data breach can expose this sensitive information to malicious actors, leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and reputational harm for both the call center and its clients. Maintaining data integrity and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations are essential for building and maintaining customer trust.
Security Measures Implemented by CRM Vendors
CRM vendors employ a multi-layered approach to protect sensitive customer data. This typically includes data encryption both in transit and at rest, using protocols like HTTPS and AES encryption. Access control mechanisms, such as role-based access control (RBAC), restrict access to sensitive data based on employee roles and responsibilities. Regular security audits and penetration testing identify vulnerabilities and ensure the effectiveness of security measures. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security, requiring multiple forms of verification before granting access to the system. Intrusion detection and prevention systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and automatically block or alert on potential threats. Data loss prevention (DLP) tools prevent sensitive data from leaving the system without authorization. Finally, regular software updates and patching address known vulnerabilities and improve overall system security.
Compliance Requirements
Call center CRM software must comply with various regulations depending on the industry and geographical location. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe mandates stringent data protection standards, requiring explicit consent for data collection and providing individuals with control over their data. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States governs the protection of health information, imposing strict rules on the handling and storage of Protected Health Information (PHI). Other relevant regulations may include the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), depending on the type of data processed.
Best Practices for Securing CRM Data
Implementing robust security practices within the call center environment is vital. This includes establishing strong password policies, requiring regular password changes, and enforcing multi-factor authentication for all users. Employee training on security awareness is crucial, educating employees about phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and safe data handling practices. Regular security audits and penetration testing help identify vulnerabilities and ensure the effectiveness of security measures. Data encryption, both in transit and at rest, protects sensitive data from unauthorized access. Access control measures restrict access to data based on roles and responsibilities, minimizing the risk of unauthorized data access. Regular backups and disaster recovery plans ensure business continuity in case of data loss or system failure. Finally, adherence to relevant compliance regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA, is essential to protect customer data and avoid legal penalties.
Conducting Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits are essential for maintaining the security of the CRM system. These audits involve a systematic review of security controls, policies, and procedures to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with relevant regulations. Audits can be conducted internally by dedicated security personnel or externally by specialized security firms. The audit process typically involves reviewing system logs, access control mechanisms, data encryption methods, and other security measures. The findings of the audit are then used to develop and implement corrective actions to address any identified vulnerabilities. The frequency of security audits should be determined based on the risk level and regulatory requirements, but generally, annual audits are recommended, with more frequent reviews for high-risk systems.
Wrap-Up
Ultimately, the implementation of CRM software in a call center environment signifies a strategic investment in improved efficiency and enhanced customer relationships. By leveraging the power of data analytics, streamlined processes, and integrated systems, businesses can significantly enhance their operational performance, boost agent productivity, and foster stronger customer loyalty. The benefits extend beyond immediate improvements, contributing to long-term growth and sustained success.