Best CRM Software for Business Success
Best CRM software for business is crucial for growth. Choosing the right system can significantly impact efficiency, customer relationships, and ultimately, profitability. This guide explores key considerations for selecting and implementing a CRM solution tailored to your specific business needs, from evaluating features and integrations to understanding security and ROI.
We’ll delve into the functionalities of top CRM platforms, comparing their strengths and weaknesses to help you make an informed decision. We will also cover essential aspects like data security, implementation strategies, and the long-term benefits of a well-integrated CRM system. Ultimately, the goal is to empower you to select a CRM that aligns perfectly with your business objectives and contributes to sustainable success.
Defining Business Needs for CRM Software
Choosing the right CRM software is crucial for business success. The ideal system seamlessly integrates with your existing workflows and scales to meet your evolving needs. Understanding your specific requirements is the first step in this process. This involves considering your business size, industry, and long-term goals.
Business Size and CRM Requirements
Different sized businesses have varying CRM needs. Small businesses often require a simple system to manage contacts, track leads, and handle basic customer interactions. Medium-sized businesses might need more advanced features like sales forecasting, marketing automation, and reporting capabilities. Large enterprises often require highly customizable, integrated CRM solutions that can manage complex data across multiple departments and locations, potentially integrating with ERP systems and other enterprise software. For example, a small bakery might only need a basic contact management system, while a large multinational corporation might require a sophisticated system with extensive customization options and integration capabilities.
Industries Benefiting from CRM Implementation
Numerous industries benefit significantly from CRM implementation. The sales and marketing departments in the technology sector, for instance, leverage CRM to track leads, manage sales pipelines, and nurture customer relationships throughout the entire customer journey, from initial contact to post-sales support. Similarly, the financial services industry relies heavily on CRM to manage client portfolios, track interactions, and comply with regulatory requirements. Healthcare providers utilize CRM to manage patient records, schedule appointments, and improve communication. The unique needs of each industry dictate the specific features and functionalities required from their CRM systems. For example, a healthcare provider’s CRM would prioritize data security and HIPAA compliance, while a technology company’s CRM might focus on lead tracking and sales pipeline management.
Key Features to Consider When Choosing CRM Software
Scalability and future growth are paramount when selecting CRM software. Consider features like user-friendliness, customizability, integration capabilities (with existing software and future potential additions), reporting and analytics, mobile accessibility, and security. A system that can adapt to your business’s evolving needs, accommodating increasing user numbers and data volume, is essential. For example, a small startup might initially need a simple CRM with basic contact management features, but as it grows, it may require more advanced features like marketing automation and sales forecasting. Choosing a scalable solution avoids the need for costly migrations or system replacements in the future.
Matching Business Needs and CRM Functionalities
| Business Need | CRM Functionality | Example | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales Management | Lead tracking, opportunity management, sales forecasting | Tracking leads from marketing campaigns, managing sales pipelines | Improved sales efficiency and forecasting accuracy |
| Marketing Automation | Email marketing, campaign management, lead nurturing | Automated email sequences, targeted marketing campaigns | Increased marketing ROI and improved lead conversion rates |
| Customer Service | Case management, ticketing system, knowledge base | Managing customer inquiries, resolving issues efficiently | Improved customer satisfaction and reduced resolution times |
| Reporting and Analytics | Sales reports, marketing analytics, customer insights | Tracking key metrics, identifying areas for improvement | Data-driven decision-making and improved business performance |
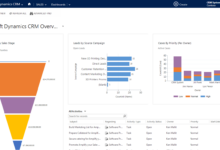
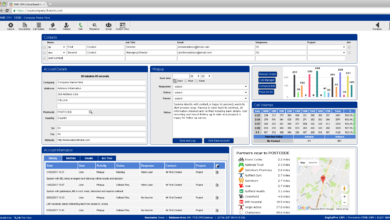
Exploring Top CRM Software Options
Choosing the right CRM can significantly impact a business’s efficiency and growth. This section compares three leading CRM platforms: Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM, considering their core functionalities, pricing, user experience, and key features. This comparative analysis aims to provide a clearer understanding of each platform’s strengths and weaknesses to aid in informed decision-making.
Salesforce: Core Functionalities, Pricing, and User Experience
Salesforce, a market leader, offers a comprehensive suite of CRM tools catering to diverse business needs. Its core functionalities include sales force automation, marketing automation, customer service, and analytics. Pricing is tiered, ranging from basic plans suitable for small businesses to enterprise-level solutions with advanced features and customized support. The pricing model is largely subscription-based, with costs varying depending on the number of users and selected features. Salesforce’s user interface, while powerful, can initially feel overwhelming due to its extensive feature set. However, with familiarity, users find its customization options and robust reporting capabilities highly beneficial. Navigation can be improved with the use of the extensive help documentation.
- Strengths: Extensive features, robust customization, strong integration capabilities, extensive app ecosystem, excellent reporting and analytics.
- Weaknesses: Steep learning curve, can be expensive, complex interface for beginners, requires dedicated IT support for complex implementations.
- User Interface and Experience: Powerful but initially complex. Customization options allow for a tailored experience, but require time and effort to master. Navigation improves with training and familiarity.
HubSpot: Core Functionalities, Pricing, and User Experience
HubSpot distinguishes itself by integrating marketing, sales, and service functionalities within a single platform. This integrated approach streamlines workflows and improves team collaboration. Its pricing model offers a freemium option, appealing to startups and small businesses, along with scaled-up paid plans for enterprises. The user interface is generally considered intuitive and user-friendly, making it easier to learn and navigate than Salesforce. The focus on user experience is reflected in its clear design and straightforward navigation.
- Strengths: Intuitive interface, integrated marketing, sales, and service tools, freemium option, strong focus on user experience, robust reporting features.
- Weaknesses: Limited customization compared to Salesforce, fewer advanced features in the lower-tier plans, some users may find the free version too limited for their needs.
- User Interface and Experience: Clean, intuitive, and easy to navigate. The user-friendly design makes it accessible to users with limited technical expertise.
Zoho CRM: Core Functionalities, Pricing, and User Experience
Zoho CRM offers a balance between functionality and affordability. It provides a solid set of CRM features at a competitive price point, making it attractive to small and medium-sized businesses. Its pricing structure is tiered, with various plans offering different levels of functionality and user capacity. The user interface is relatively straightforward, though some users might find it less visually appealing than HubSpot’s. Navigation is generally smooth and intuitive, making it a good option for businesses looking for a cost-effective solution.
- Strengths: Affordable pricing, wide range of features, good value for money, relatively easy to learn and use, strong integration with other Zoho applications.
- Weaknesses: Fewer advanced features compared to Salesforce and HubSpot, reporting and analytics capabilities might not be as robust, customization options are more limited.
- User Interface and Experience: Clean and straightforward, but might lack the visual appeal and advanced customization options of other platforms. Navigation is generally intuitive and easy to learn.
Cost and Return on Investment (ROI)
Choosing the right CRM involves careful consideration of its cost and the potential return on that investment. Understanding different pricing models and how to calculate ROI is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your business’s financial goals. A well-planned CRM implementation can significantly improve efficiency and boost revenue, but a poorly planned one can lead to wasted resources.
Different CRM pricing models cater to various business sizes and needs. Understanding these models is key to choosing a system that fits your budget and anticipated usage.
CRM Pricing Models
CRMs typically operate on either a subscription-based model or a one-time purchase model. Subscription-based models offer different tiers with varying features and user limits, usually billed monthly or annually. This allows for scalability; businesses can upgrade or downgrade their plans as their needs change. One-time purchases, on the other hand, involve a single upfront payment for the software license. However, this often requires ongoing maintenance costs and may lack the flexibility of subscription-based models. Some vendors offer hybrid models combining elements of both. For example, a base software license might be purchased upfront, with additional features or support offered as monthly subscriptions.
Calculating CRM ROI
Calculating the ROI of a CRM investment requires a clear understanding of both costs and benefits. Costs include the initial software purchase or subscription fees, implementation costs (consulting, training, data migration), ongoing maintenance fees, and potential staff time dedicated to system management. Benefits can include increased sales, improved customer satisfaction, reduced operational costs (e.g., through automation), and enhanced data-driven decision-making. A simplified ROI calculation can be expressed as:
ROI = (Net Benefits – Total Costs) / Total Costs * 100%
For example, a business invests $10,000 in CRM software and implementation. Over the next year, they see a $20,000 increase in sales directly attributable to improved customer relationship management facilitated by the CRM. Their ROI would be:
ROI = ($20,000 – $10,000) / $10,000 * 100% = 100%
This indicates a strong return on investment. However, it’s crucial to consider less quantifiable benefits, such as improved customer loyalty and employee satisfaction, which are harder to assign monetary values to but still contribute significantly to the overall value of the CRM.
Factors Influencing CRM Costs
Several factors significantly influence the overall cost of CRM implementation and maintenance. These include the size of the business and the number of users, the chosen CRM features and functionalities (e.g., marketing automation, customer service tools), the complexity of integration with existing systems, the level of customization required, and the ongoing support and maintenance contracts. A larger business with complex needs will naturally incur higher costs than a smaller business with simpler requirements. The level of customization required also plays a crucial role, as extensive customization necessitates more development time and expertise, leading to increased expenses.
Creating a Cost-Benefit Analysis
A cost-benefit analysis is a structured approach to comparing the costs and benefits of different CRM options. This involves listing all anticipated costs (software licenses, implementation, training, maintenance) and benefits (increased sales, improved efficiency, reduced operational costs). Assign monetary values wherever possible to quantify the benefits. Then, compare the net present value (NPV) or internal rate of return (IRR) of different CRM solutions to determine the most financially viable option. For example, a table could compare three different CRM options, showing their projected costs over three years, and the estimated revenue increase generated by each, enabling a direct comparison of their ROI. A simple example would include columns for CRM Name, Initial Cost, Annual Cost, Estimated Revenue Increase (Year 1), Estimated Revenue Increase (Year 2), Estimated Revenue Increase (Year 3), and Total ROI over three years. This allows for a clear and concise comparison, enabling informed decision-making based on financial projections.
Illustrative Examples of CRM Software in Action
Seeing CRM software in action helps solidify its benefits. Real-world examples demonstrate how different businesses, regardless of size, can leverage CRM features to improve efficiency and customer relationships. The following scenarios illustrate the practical application of CRM across various business contexts.
Small Business Success with CRM: Enhanced Customer Relationships and Sales
A small bakery, “Sweet Success,” uses a CRM system to manage customer orders, track preferences (like favorite cake flavors or dietary restrictions), and send personalized birthday messages. The CRM’s integrated calendar reminds staff of upcoming orders and allows for efficient scheduling of deliveries. By leveraging the lead management feature, Sweet Success effectively tracks customer interactions, converting initial inquiries into loyal customers through targeted marketing campaigns based on their preferences. The sales pipeline visualization feature provides a clear overview of the sales process, enabling the bakery to identify potential bottlenecks and proactively address them. This resulted in a 20% increase in repeat business within six months of implementing the CRM.
Large Enterprise CRM Implementation: Operational Efficiency and Customer Segmentation
A large telecommunications company, “ConnectAll,” uses a sophisticated CRM system to manage millions of customer accounts. The system enables highly effective customer segmentation, allowing ConnectAll to tailor marketing campaigns and service offerings to specific customer groups based on demographics, usage patterns, and value. This improved targeting has increased customer retention rates and reduced churn significantly. Furthermore, the CRM’s automated workflows streamline internal processes, such as lead assignment, issue resolution, and billing, significantly improving operational efficiency. The integrated reporting and analytics dashboards provide valuable insights into customer behavior and sales performance, enabling data-driven decision-making. ConnectAll reported a 15% reduction in operational costs and a 10% increase in customer lifetime value within a year of full CRM deployment.
Conclusion
Selecting the best CRM software for your business requires careful consideration of various factors, from initial needs assessment to long-term scalability and security. By understanding your specific requirements, researching available options, and planning for a smooth implementation, you can harness the power of a CRM to streamline operations, enhance customer relationships, and drive significant business growth. Remember, the right CRM is an investment that pays dividends in efficiency and profitability.